It is estimated that 160,000 Americans die of lung cancer every year. Researchers predict that a lung cancer screening test could eventually prevent between 8,000 and 22,000 lung cancer deaths per year.
Lung cancer screening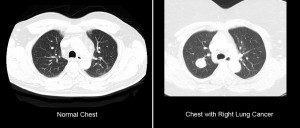
Screening for cancer means testing for cancer before there are any symptoms. Screening for
some types of cancer has reduced deaths by early detection and treatment. There is now a
test that can reduce death from lung cancer through early detection. Guidelines recommending annual low-dose CT lung cancer screening for older smokers have been approved by the US Preventive Services Task Force. The recommendations apply to individuals aged between 55 and 80 who are at high risk for lung cancer as a result of heavy smoking.
The test is not recommended for everyone and it has risks as well as benefits. Here are key points you may want to use in discussion with your patients who may be at risk for lung cancer or are worried about their risk for lung cancer.
Candidates for lung cancer screening will have to pertain in the following groups :
a current or former smoker
and in the age group from 55 to 74 years
and with a smoking history of at least 30 pack-years (this means 1 pack a day for 30
years, 2 packs a day for 15 years, etc.)
Only Low Dose CT scans are recommended for screening. Chest X-rays are not recommended for lung cancer screening. There is some radiation risk with a CT scan and you may need to have additional tests and procedures. You should go to a facility that uses “best practices” for lung cancer screening. This means a hospital or screening center that has a team of experts who will clearly explain the procedure to you. The team should tell you about all the risks and benefits of the screening. They should also discuss what the results can mean and how they will follow up with you after the initial screening.